目录
0 基本元素 primitives
1 曲线 2DLines
2 二维图形 Patches
3 组合 Collection
4 图像 Image0 基本元素 - primitives
各容器中可能会包含多种基本要素-primitives。本章重点介绍下 primitives 的几种类型:曲线,二位图形(矩形、多边形、楔形),图像 (其中文本较为复杂,会在之后单独详细说明。)
1 曲线 2DLines
在matplotlib中曲线的绘制,主要是通过类 matplotlib.lines.Line2D 来完成的(它的基类: matplotlib.artist.Artist)。matplotlib 中线 line 的含义:它表示的可以是连接所有顶点的实线样式,也可以是每个顶点的标记。此外,这条线也会受到绘画风格的影响,比如,我们可以创建虚线种类的线。它的构造函数:
class matplotlib.lines.Line2D(xdata, ydata, linewidth=None, linestyle=None, color=None, marker=None, markersize=None, markeredgewidth=None, markeredgecolor=None, markerfacecolor=None, markerfacecoloralt='none', fillstyle=None, antialiased=None, dash_capstyle=None, solid_capstyle=None, dash_joinstyle=None, solid_joinstyle=None, pickradius=5, drawstyle=None, markevery=None, **kwargs)其中常用的的参数有:
- xdata: 需要绘制的line中点的在x轴上的取值,若忽略,则默认为range(1,len(ydata)+1)
- ydata: 需要绘制的line中点的在y轴上的取值
- linewidth: 线条的宽度
- linestyle: 线型
- color: 线条的颜色
- marker: 点的标记,详细可参考markers API
- markersize: 标记的size
1.1 如何绘制 lines
方法 1: pyplot方法绘制
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = range(0,5)
y = [2,5,7,8,10]
plt.plot(x,y);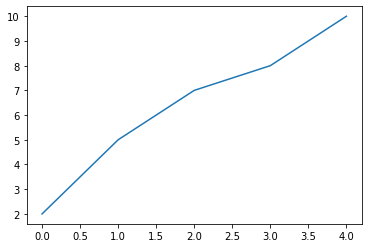
方法 2: Line2D对象绘制
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
x = range(0,5)
y = [2,5,7,8,10]
line = Line2D(x, y)
ax.add_line(line)
ax.set_xlim(min(x), max(x))
ax.set_ylim(min(y), max(y))
plt.show()
1.2 设置 Line2D 属性的方式
方法 1: 直接在plot()函数中设置
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = range(0,5)
y = [2,5,7,8,10]
plt.plot(x,y, linewidth=10); # 设置线的粗细参数为10
方法 2:通过获得线对象,对线对象进行设置
x = range(0,5)
y = [2,5,7,8,10]
line, = plt.plot(x, y, '-')
line.set_antialiased(False) # 关闭抗锯齿功能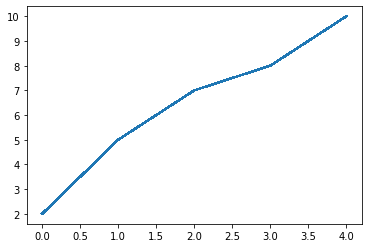
方法 3: 获得线属性,使用setp()函数设置
x = range(0,5)
y = [2,5,7,8,10]
lines = plt.plot(x, y)
plt.setp(lines, color='r', linewidth=10);
1.3 errorbar绘制误差折线图
pyplot里有个专门绘制误差线的功能,通过errorbar类实现,它的构造函数:
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar(x, y, yerr=None, xerr=None, fmt='', ecolor=None, elinewidth=None, capsize=None, barsabove=False, lolims=False, uplims=False, xlolims=False, xuplims=False, errorevery=1, capthick=None, *, data=None, **kwargs)其中最主要的参数是前几个:
- x:需要绘制的line中点的在x轴上的取值
- y:需要绘制的line中点的在y轴上的取值
- yerr:指定y轴水平的误差
- xerr:指定x轴水平的误差
- fmt:指定折线图中某个点的颜色,形状,线条风格,例如‘co--’
- ecolor:指定error bar的颜色
- elinewidth:指定error bar的线条宽度
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
x = np.arange(10)
y = 2.5 * np.sin(x / 20 * np.pi)
yerr = np.linspace(0.05, 0.2, 10)
plt.errorbar(x, y + 3, yerr=yerr, label='both limits (default)');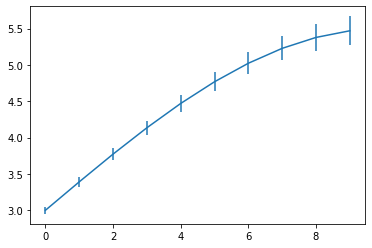
2 二维图形 Patches
matplotlib.patches.Patch类是二维图形类。它的基类是matplotlib.artist.Artist,它的构造函数:
Patch(edgecolor=None, facecolor=None, color=None, linewidth=None, linestyle=None, antialiased=None, hatch=None, fill=True, capstyle=None, joinstyle=None, **kwargs)2.1 Rectangle 矩形
Rectangle矩形类在官网中的定义是: 通过锚点xy及其宽度和高度生成。 Rectangle本身的主要比较简单,即xy控制锚点,width和height分别控制宽和高。它的构造函数:class matplotlib.patches.Rectangle(xy, width, height, angle=0.0, **kwargs)
直方图 hist 方法
matplotlib.pyplot.hist(x,bins=None,range=None, density=None, bottom=None, histtype='bar', align='mid', log=False, color=None, label=None, stacked=False, normed=None)- x: 数据集,最终的直方图将对数据集进行统计
- bins: 统计的区间分布
- range: tuple, 显示的区间,range在没有给出bins时生效
- density: bool,默认为false,显示的是频数统计结果,为True则显示频率统计结果,这里需要注意,频率统计结果=区间数目/(总数*区间宽度),和normed效果一致,官方推荐使用density
- histtype: 可选{'bar', 'barstacked', 'step', 'stepfilled'}之一,默认为bar,推荐使用默认配置,step使用的是梯状,stepfilled则会对梯状内部进行填充,效果与bar类似
- align: 可选{'left', 'mid', 'right'}之一,默认为'mid',控制柱状图的水平分布,left或者right,会有部分空白区域,推荐使用默认
- log: bool,默认False,即y坐标轴是否选择指数刻度
- stacked: bool,默认为False,是否为堆积状图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x=np.random.randint(0,100,100) #生成[0-100)之间的100个数据,即 数据集
bins=np.arange(0,101,10) #设置连续的边界值,即直方图的分布区间[0,10),[10,20)...
plt.hist(x,bins,color='fuchsia',alpha=0.5)#alpha设置透明度,0为完全透明
plt.xlabel('scores')
plt.ylabel('count')
plt.xlim(0,100)#设置x轴分布范围
plt.show()
直方图 Rectangle 方法
import pandas as pd
import re
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['data'])
df.loc[:,'data'] = x
df['fenzu'] = pd.cut(df['data'], bins=bins, right = False,include_lowest=True)
df_cnt = df['fenzu'].value_counts().reset_index()
df_cnt.loc[:,'mini'] = df_cnt['index'].astype(str).map(lambda x:re.findall('\[(.*)\,',x)[0]).astype(int)
df_cnt.loc[:,'maxi'] = df_cnt['index'].astype(str).map(lambda x:re.findall('\,(.*)\)',x)[0]).astype(int)
df_cnt.loc[:,'width'] = df_cnt['maxi']- df_cnt['mini']
df_cnt.sort_values('mini',ascending = True,inplace = True)
df_cnt.reset_index(inplace = True,drop = True)
#用Rectangle把hist绘制出来
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
for i in df_cnt.index:
rect = plt.Rectangle((df_cnt.loc[i,'mini'],0),df_cnt.loc[i,'width'],df_cnt.loc[i,'fenzu'])
ax1.add_patch(rect)
ax1.set_xlim(0, 100)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 16)
plt.show()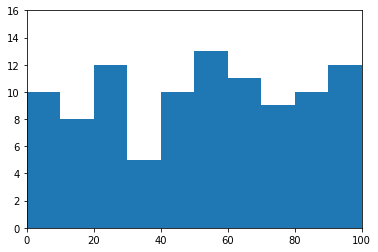
柱状图 bar 方法
bar(left, height, alpha=1, width=0.8, color=, edgecolor=, label=, lw=3)
下面是一些常用的参数:
- left:x轴的位置序列,一般采用range函数产生一个序列,但是有时候可以是字符串
- height:y轴的数值序列,也就是柱形图的高度,一般就是我们需要展示的数据;
- alpha:透明度,值越小越透明
- width:为柱形图的宽度,一般这是为0.8即可;
- color或facecolor:柱形图填充的颜色;
- edgecolor:图形边缘颜色
- label:解释每个图像代表的含义,这个参数是为legend()函数做铺垫的,表示该次bar的标签
# bar绘制柱状图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y = range(1,17)
plt.bar(np.arange(16), y, alpha=0.5, width=0.5, color='yellow', edgecolor='red', label='The First Bar', lw=3);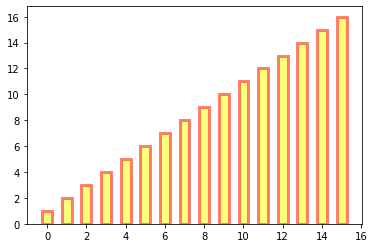
柱状图 rectangle 方法
# Rectangle矩形类绘制柱状图
#import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
for i in range(1,17):
rect = plt.Rectangle((i+0.25,0),0.5,i)
ax1.add_patch(rect)
ax1.set_xlim(0, 16)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 16)
plt.show()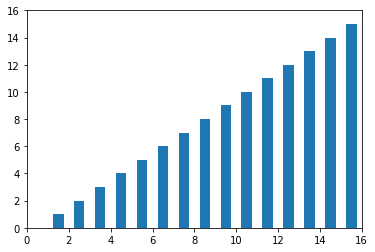
2.2 Ploygan 多边形
matplotlib.patches.Polygon类是多边形类。其基类是matplotlib.patches.Patch,它的构造函数:
class matplotlib.patches.Polygon(xy, closed=True, **kwargs)xy是一个N×2的numpy array,为多边形的顶点。closed为True则指定多边形将起点和终点重合从而显式关闭多边形。
matplotlib.patches.Polygon类中常用的是fill类,它是基于xy绘制一个填充的多边形,它的定义:
matplotlib.pyplot.fill(*args, data=None, **kwargs)参数说明 : 关于x、y和color的序列,其中color是可选的参数,每个多边形都是由其节点的x和y位置列表定义的,后面可以选择一个颜色说明符。您可以通过提供多个x、y、[颜色]组来绘制多个多边形。
# 用fill来绘制图形
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 5 * np.pi, 1000)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.sin(2 * x)
plt.fill(x, y1, color = "g", alpha = 0.3);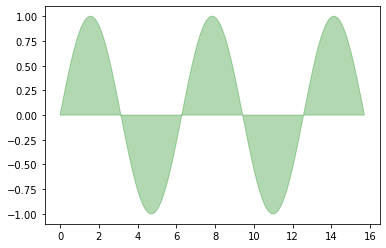
2.3 Wedge 楔形
matplotlib.patches.Polygon类是多边形类。其基类是matplotlib.patches.Patch,它的构造函数:
class matplotlib.patches.Wedge(center, r, theta1, theta2, width=None, **kwargs)一个Wedge-契形 是以坐标x,y为中心,半径为r,从θ1扫到θ2(单位是度)。
如果宽度给定,则从内半径r -宽度到外半径r画出部分楔形。wedge中比较常见的是绘制饼状图。
matplotlib.pyplot.pie语法:
matplotlib.pyplot.pie(x, explode=None, labels=None, colors=None, autopct=None, pctdistance=0.6, shadow=False, labeldistance=1.1, startangle=0, radius=1, counterclock=True, wedgeprops=None, textprops=None, center=0, 0, frame=False, rotatelabels=False, *, normalize=None, data=None)制作数据x的饼图,每个楔子的面积用x/sum(x)表示。
其中最主要的参数是前4个:
- x:契型的形状,一维数组。
- explode:如果不是等于None,则是一个len(x)数组,它指定用于偏移每个楔形块的半径的分数。
- labels:用于指定每个契型块的标记,取值是列表或为None。
- colors:饼图循环使用的颜色序列。如果取值为None,将使用当前活动循环中的颜色。
- startangle:饼状图开始的绘制的角度。
pie绘制饼状图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
labels = 'Frogs', 'Hogs', 'Dogs', 'Logs'
sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10]
explode = (0, 0.1, 0, 0)
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.pie(sizes, explode=explode, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True, startangle=90)
ax1.axis('equal') # Equal aspect ratio ensures that pie is drawn as a circle.
plt.show()
wedge绘制饼图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Circle, Wedge
from matplotlib.collections import PatchCollection
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
theta1 = 0
sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10]
patches = []
patches += [
Wedge((0.3, 0.3), .2, 0, 54), # Full circle
Wedge((0.3, 0.3), .2, 54, 162), # Full ring
Wedge((0.3, 0.3), .2, 162, 324), # Full sector
Wedge((0.3, 0.3), .2, 324, 360), # Ring sector
]
colors = 100 * np.random.rand(len(patches))
p = PatchCollection(patches, alpha=0.4)
p.set_array(colors)
ax1.add_collection(p)
plt.show()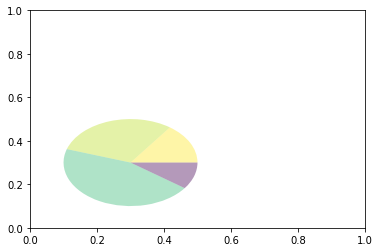
3 组合 Collections
collections类是用来绘制一组对象的集合,collections有许多不同的子类,如RegularPolyCollection, CircleCollection, Pathcollection, 分别对应不同的集合子类型。其中比较常用的就是散点图,它是属于PathCollection子类,scatter方法提供了该类的封装,根据x与y绘制不同大小或颜色标记的散点图。 它的构造方法:
Axes.scatter(self, x, y, s=None, c=None, marker=None, cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, verts=, edgecolors=None, *, plotnonfinite=False, data=None, **kwargs)其中最主要的参数是前5个:
- x:数据点x轴的位置
- y:数据点y轴的位置
- s:尺寸大小
- c:可以是单个颜色格式的字符串,也可以是一系列颜色
- marker: 标记的类型
# 用scatter绘制散点图
x = [0,2,4,6,8,10]
y = [10]*len(x)
s = [20*2**n for n in range(len(x))]
plt.scatter(x,y,s=s)
plt.show()
4 图像 Images
images是matplotlib中绘制image图像的类,其中最常用的imshow可以根据数组绘制成图像,它的构造函数:
class matplotlib.image.AxesImage(ax, cmap=None, norm=None, interpolation=None, origin=None, extent=None, filternorm=True, filterrad=4.0, resample=False, **kwargs)imshow根据数组绘制图像
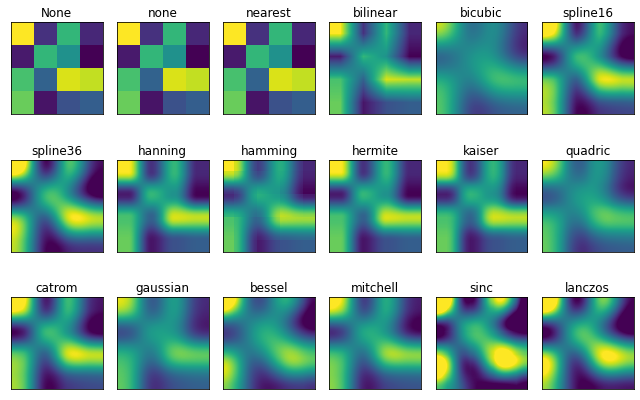
matplotlib.pyplot.imshow(X, cmap=None, norm=None, aspect=None, interpolation=None, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, origin=None, extent=None, shape=, filternorm=1, filterrad=4.0, imlim=, resample=None, url=None, *, data=None, **kwargs)使用imshow画图时首先需要传入一个数组,数组对应的是空间内的像素位置和像素点的值,interpolation参数可以设置不同的差值方法,具体效果如下。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
methods = [None, 'none', 'nearest', 'bilinear', 'bicubic', 'spline16',
'spline36', 'hanning', 'hamming', 'hermite', 'kaiser', 'quadric',
'catrom', 'gaussian', 'bessel', 'mitchell', 'sinc', 'lanczos']
grid = np.random.rand(4, 4)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=6, figsize=(9, 6),
subplot_kw={'xticks': [], 'yticks': []})
for ax, interp_method in zip(axs.flat, methods):
ax.imshow(grid, interpolation=interp_method, cmap='viridis')
ax.set_title(str(interp_method))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()